Threat Overview
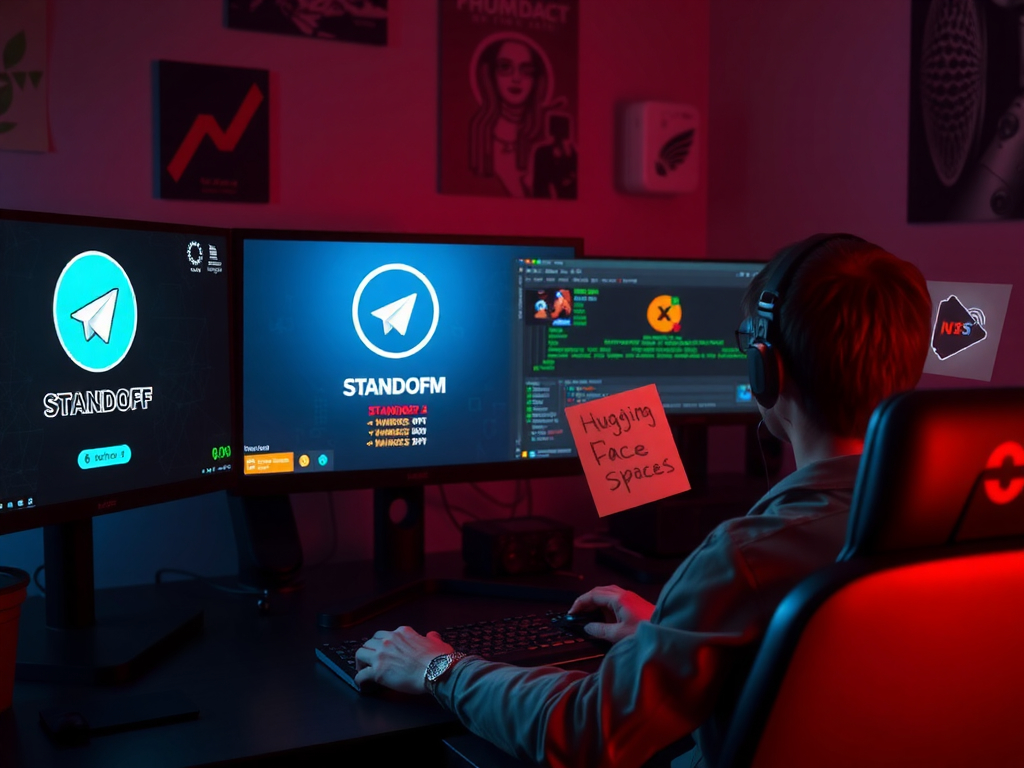
The security landscape is ever-evolving, with new threats emerging constantly. One such threat that has recently come to light is Blitz Malware. This Windows-based malware was discovered in 2024 and consists of a downloader and bot payload. The latest version of Blitz Malware was spread through backdoored game cheats for the popular game Standoff 2, distributed via Telegram. This method of distribution underscores the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the need for heightened vigilance among users.
Blitz Malware employs a multi-faceted approach to carry out its malicious activities. It abuses Hugging Face Spaces to host components of its Command and Control (C2) infrastructure and payloads. This abuse of legitimate services is a common tactic among advanced threat actors, as it helps them evade detection by security solutions that rely on blacklisting known malicious domains.
The primary functions of Blitz Malware include information stealing and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. The malware is designed to exfiltrate sensitive information from infected systems, which can then be used for various malicious purposes, including financial fraud and identity theft. Additionally, the DDoS capabilities of Blitz Malware allow it to overwhelm targeted servers with traffic, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users.
In addition to these core functions, Blitz Malware also deploys an XMRig cryptocurrency miner as follow-up malware. Cryptocurrency mining can significantly impact system performance, leading to increased energy consumption and hardware wear and tear. Furthermore, the resources used for mining are often diverted from legitimate tasks, further exacerbating the problem.
By May 2025, the developer of Blitz Malware claimed to have abandoned the project. However, this does not necessarily mean that the threat has been neutralized. Abandoned malware projects can sometimes be picked up by other threat actors, who may modify and reuse them for their own purposes. Therefore, it is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in defending against such threats.
Geographical Distribution
The geographical distribution of Blitz Malware infections provides valuable insights into the target demographics of this threat. Russia accounted for the highest number of infections among 289 victims across 26 countries. This high concentration of infections in a single country suggests that the malware may have been tailored to exploit specific vulnerabilities or behaviors prevalent in that region.
Recommendations
In light of the Blitz Malware threat, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect against similar attacks in the future. Here are some recommendations for mitigating the risk posed by Blitz Malware and other advanced threats:
- User Education: Educate users about the risks associated with downloading game cheats from unofficial sources. Emphasize the importance of obtaining software from trusted vendors and avoiding suspicious links and downloads.
- Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of malware within an organization. By isolating critical systems and data, you can reduce the potential impact of a successful attack.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity. Regularly update the signature database to ensure that the latest threats are detected and blocked.
-
Endpoint Protection: Use advanced endpoint protection solutions that employ behavior-based detection to identify and block malware, even if it has not been previously seen.
-
Regular Updates: Keep all software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches. Vulnerabilities in outdated software can be exploited by threat actors to gain access to your network.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to ensure that you are prepared to respond quickly and effectively to a security breach. This includes having a team of trained personnel who can handle the technical and communication aspects of a response.
-
Monitoring and Analysis: Continuously monitor your network for signs of suspicious activity. Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems to analyze logs and identify potential threats in real-time.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all user accounts to add an extra layer of security. This makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access to sensitive data, even if they have obtained valid credentials.
-
Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of critical data and systems. In the event of a ransomware attack or data breach, having up-to-date backups can help you quickly restore operations and minimize downtime.
-
Third-Party Risk Management: Assess the security posture of third-party vendors and partners. Ensure that they adhere to the same security standards as your organization to prevent supply chain attacks.
Conclusion
The emergence of Blitz Malware serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threat posed by advanced cyber threats. By understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by these threats, organizations can better prepare themselves to defend against them. Implementing robust security measures, educating users, and maintaining a proactive approach to cybersecurity are crucial steps in mitigating the risk of falling victim to such attacks.
For more detailed information on Blitz Malware, including technical analysis and indicators of compromise (IOCs), please refer to the following resources:
- Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 Report: Blitz Malware – A Tale of Game Cheats and Code Repositories
- AlienVault OTX Pulse: Blitz Malware Pulse
These resources provide in-depth analysis and actionable insights to help security professionals stay ahead of the curve in defending against Blitz Malware and similar threats.
Discover more from ESSGroup
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.