Discover more from ESSGroup
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

Hackers Use Microsoft Management Console to Deliver Malicious Payloads.
As outlined in a recent threat report, hackers have been exploiting the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) to deliver backdoor payloads on Windows systems. This sophisticated campaign employs advanced obfuscation techniques and Microsoft Common Console Document (MSC) files to evade detection.
The attackers, believed to be nation-state actors, use the MMC to drop a stealthy backdoor payload that allows them to maintain persistent access to compromised systems. The malicious activity is said to target organizations in various industries, including government agencies, financial institutions, and technology companies.
The hackers responsible for this campaign have demonstrated expertise in evasive techniques and persistence.
Their tactics include:
The attackers have leveraged various tools and infrastructure, including:
Some notable characteristics of this campaign include:
To mitigate the risks associated with this campaign, organizations can take the following measures:
The tactics employed by this actor group highlight the need for organizations to remain vigilant against emerging threats. It is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest threat reports, maintain robust security controls, and prioritize employee education and awareness.
Resources:
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting
industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's

Threat Report Overview
This week’s cybersecurity landscape presents a mix of positive developments and concerning threats. The intelligence update, published by AlienVault on May 16, 2025, provides a comprehensive overview of recent events that highlight both the successes and challenges faced in the realm of cybersecurity.
Positive Developments
Global authorities have made significant strides in combating cybercrime. A major botnet was disrupted, which is a crucial step in reducing the number of compromised systems used for malicious activities. This disruption not only mitigates immediate threats but also helps in gathering intelligence on the botnet’s infrastructure and operators.
In another positive development, law enforcement agencies successfully arrested a key ransomware actor. Ransomware attacks have been a growing concern, causing significant financial losses and operational disruptions for organizations worldwide. The arrest of this individual is a major victory in the ongoing battle against ransomware.
Additionally, authorities dismantled a dark web marketplace. These marketplaces often serve as hubs for the sale of stolen data, malware, and other illicit goods. Shutting down such platforms disrupts criminal operations and makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to conduct their activities.
Negative Developments
Despite these successes, there have been concerning developments in the cybersecurity landscape. A malicious NPM package was discovered hiding multi-stage malware using Unicode and Google Calendar. This sophisticated attack method demonstrates the evolving tactics of cybercriminals, who are constantly finding new ways to bypass security measures.
The use of Unicode and Google Calendar in this attack highlights the importance of staying vigilant against emerging threats. Organizations must ensure that their security protocols are up-to-date and capable of detecting such advanced attacks.
Most Concerning Development
The most alarming development involves cyberspies exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in Output Messenger to target Kurdish military users in Iraq. This incident showcases the increased capabilities of the Marbled Dust threat group, which is known for its sophisticated and targeted cyber operations.
Zero-day vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they exploit flaws that are unknown to the software vendor, making them difficult to detect and mitigate. The targeting of military users underscores the strategic importance of these attacks, which can have significant geopolitical implications.
Recommendations
In light of these developments, it is crucial for organizations to adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Here are some recommendations to enhance security posture:
Monitor Network Traffic: Use advanced threat detection tools to monitor network traffic for any suspicious activities. Early detection can help in mitigating potential threats before they cause significant damage.
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Perform regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities in the organization’s infrastructure. This helps in maintaining a robust security posture.
Educate Employees: Provide regular training and awareness programs for employees on cybersecurity best practices. Human error is often a weak link in the security chain, and educating employees can help in reducing the risk of successful attacks.
Use Secure Communication Channels: Ensure that all communication channels are secure and encrypted. This helps in protecting sensitive information from being intercepted or tampered with by malicious actors.
Collaborate with Law Enforcement: Work closely with law enforcement agencies to share threat intelligence and collaborate on cybersecurity initiatives. This can help in staying ahead of emerging threats and enhancing overall security.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with both positive developments and concerning threats. While global authorities have made significant strides in combating cybercrime, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to security. By adopting best practices and staying informed about the latest threats, organizations can enhance their security posture and protect against emerging risks.
For more detailed information, please refer to the following external references:
https://www.sentinelone.com/blog/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-in-cybersecurity-week-20-6
https://otx.alienvault.com/pulse/682768bfc09a2c586edd469a
Please check the following page for additional information:
https://www.sentinelone.com/blog/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-in-cybersecurity-week-20-6
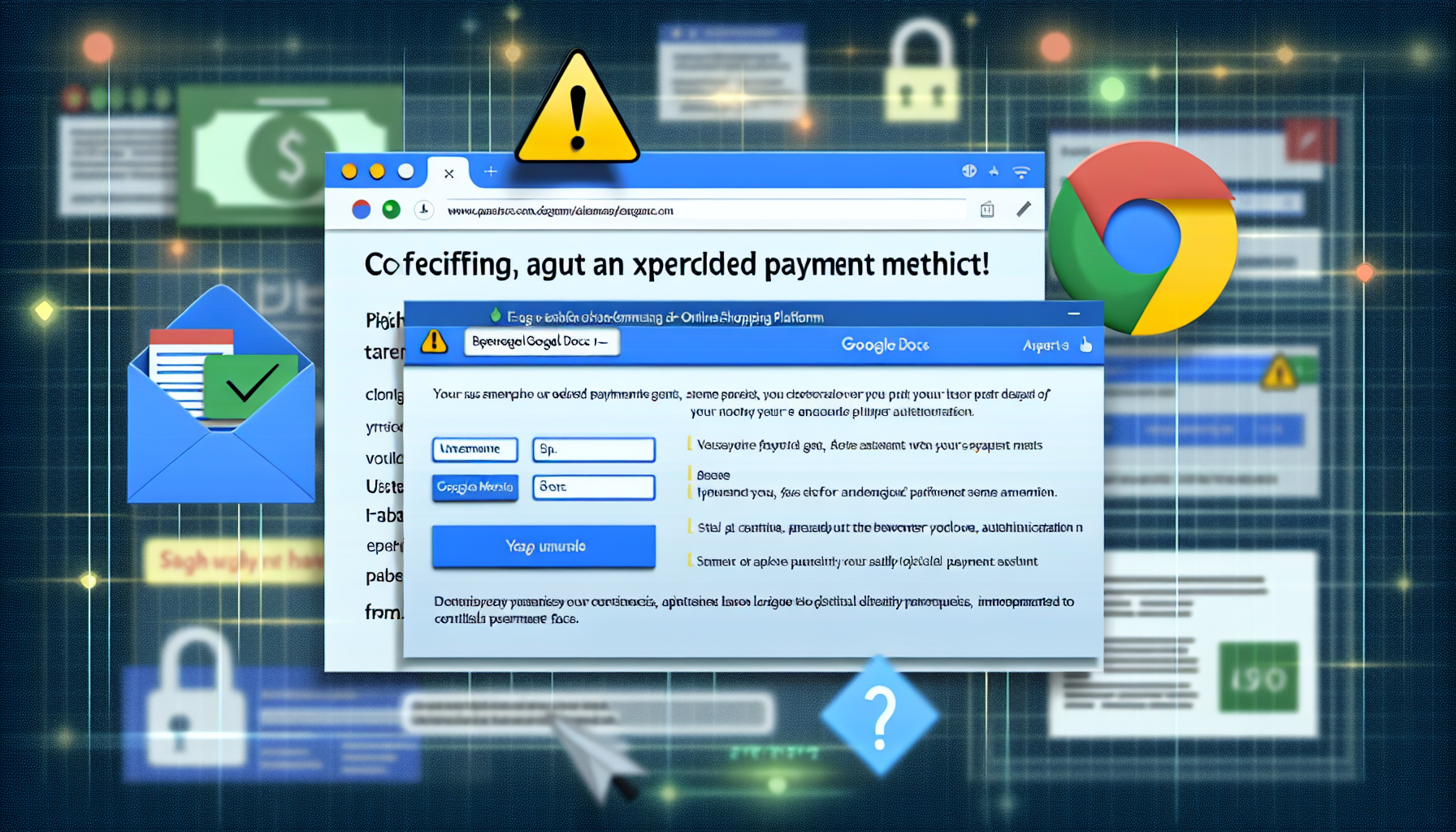
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, a new phishing scheme targeting Amazon Prime users has been identified. This sophisticated campaign aims to steal login credentials, verification information, and payment data, making it a significant concern for both individual users and the broader technology sector.
The threat report, published by AlienVault on February 18, 2025, provides a detailed analysis of this phishing scheme. The attack begins with a spoofed email that claims the user’s payment method has expired. This initial contact is designed to create a sense of urgency, prompting users to take immediate action. Clicking the update button in the email redirects victims to a fake Amazon security alert hosted on Google Docs. From there, they are led to a fraudulent login page where personal details, address information, and payment card data are requested.
This phishing campaign is particularly dangerous due to its resemblance to legitimate Amazon processes. The use of familiar branding and the mimicry of standard security procedures make it difficult for unsuspecting users to distinguish between genuine communications and malicious attempts. The sophistication of this scheme underscores the need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures.
The report highlights several key tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by the threat actors. These include social engineering through spoofed emails, the use of legitimate-looking documents hosted on trusted platforms like Google Docs, and the creation of convincing fake login pages. The ultimate goal is to bypass security measures and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
To mitigate the risks associated with this phishing campaign, users are advised to follow several best practices:
The technology sector, which includes private entities related to research, development, manufacturing, and distribution of electronics, software, computers, and information technology products, is particularly vulnerable to such attacks. The interconnected nature of modern technologies means that a breach in one area can have far-reaching consequences. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations within this sector to implement comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
The report by AlienVault provides valuable insights into the TTPs used in this phishing campaign and offers recommendations for mitigation. By understanding these tactics, users and organizations can better protect themselves against similar threats in the future. The confidence level of 100% and the reliability rating of A indicate that this report is completely trustworthy.
For additional information, you can refer to the external references provided in the report:
In conclusion, the Amazon Phish Hunts for Security Answers and Payment Information report serves as a critical reminder of the ongoing threat posed by phishing attacks. By staying vigilant, educating ourselves, and implementing robust security measures, we can better protect our personal information and safeguard against these malicious schemes.

Threat Overview
The Security Operations Center (SOC) has recently identified a significant threat report published by CyberHunter_NL on March 28, 2025. The report, titled ‘The Shelby Strategy,’ provides an in-depth analysis of emerging cyber threats and the tactics employed by malicious actors. This report is critical for understanding the current threat landscape and implementing robust security measures to protect against potential attacks.
Threat Report Details
The Shelby Strategy report is highly reliable, with a confidence level of 100% and a reliability rating of A – Completely reliable. It contains 89 connected elements, indicating a comprehensive analysis of various threat vectors and attack techniques. The report does not have any revoke status, ensuring that the information provided is current and actionable.
The external references included in the report are essential for further investigation and understanding. These references provide additional context and technical details about the threats discussed:
For additional information, please visit the following page: https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/the-shelby-strategy.
Threat Actor Group
The report provides a short description of the actor group responsible for these threats. While specific details about the actor group are not disclosed in this summary, it is crucial to note that understanding the motivations and capabilities of threat actors is essential for developing effective defense strategies.
Short Description of the Report
The Shelby Strategy report delves into the sophisticated tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by cybercriminals. It highlights the evolving nature of cyber threats and emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation of security measures. The report covers various aspects of cybersecurity, including but not limited to:
Recommendations for Mitigation
To mitigate the risks associated with these threats, the SOC recommends the following actions:
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Perform regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in your infrastructure.
Employee Training: Provide ongoing training for employees on recognizing and responding to phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics.
Use Advanced Threat Detection Tools: Deploy advanced threat detection tools that can identify and respond to suspicious activities in real-time.
Establish an Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to quickly and effectively address any security breaches or incidents.
Monitor Network Traffic: Continuously monitor network traffic for unusual activity and set up alerts for potential threats.
Conclusion
The Shelby Strategy report by CyberHunter_NL is a valuable resource for understanding the current cyber threat landscape and implementing effective security measures. By staying informed about emerging threats and adopting best practices, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyber attacks. The SOC will continue to monitor the threat landscape and provide updates as new information becomes available.
For more detailed information, please refer to the full report at https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/the-shelby-strategy.

Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.