Discover more from ESSGroup
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
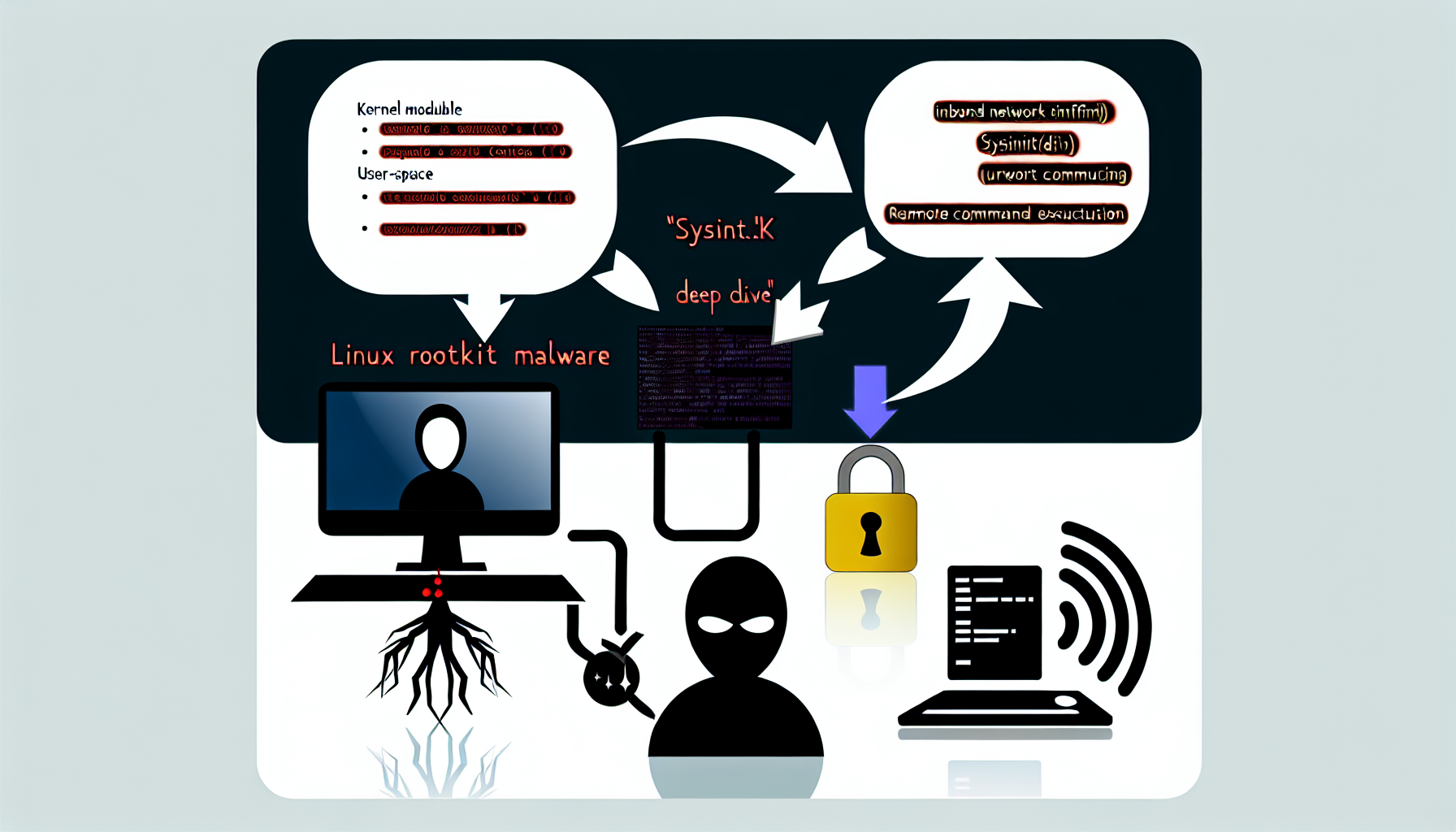
Threat Overview
A recent threat report published by AlienVault provides insights into a malicious Linux rootkit malware that has been used to compromise CentOS systems.
The report, titled “Deep Dive Into a Linux Rootkit Malware”, highlights the potential dangers posed by this malware and its capabilities.
Malware Analysis
The analysis examines a Linux rootkit malware consisting of two components: a kernel module (sysinitd.ko) and a user-space binary (sysinitd). The kernel module hijacks inbound network traffic using Netfilter hooks, creates procfs entries for communication, and starts the user-space process. Meanwhile, the user-space component disguises itself as ‘bash’, enabling remote command execution with root privileges.
Initiation of Communication
Attackers initiate communication using a special ‘attack-init’ packet, allowing them to send encrypted commands to control the compromised system. The malware’s initialization process involves binding system calls and intercepting select network protocols.
Tactics Employed
The report sheds light on the tactics employed by attackers to deploy this malware:
* Remote compromise of systems to install malicious kernel modules.
* Disguising malware components to evade detection.
* Leveraging system privileges to execute arbitrary commands.
Recommendations
Based on the threat report, several recommendations can be made for enhancing cybersecurity measures:
1. Regular Patching and Updates: Ensure CentOS systems are up-to-date to protect against exploited vulnerabilities.
2. Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS): Implementing NIDS can help detect unusual network activity and anomalies.
3. Endpoint Protection: Deploy robust endpoint protection solutions that can identify rootkit malware and prevent its installation.
4. Least Privilege Principle: Implement the principle of least privilege to minimize potential damage from compromised accounts.
5. Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of critical data to facilitate swift recovery in case of an attack.
Resources
The full threat report can be accessed here:
https://www.fortinet.com/blog/threat-research/deep-dive-into-a-linux-rootkit-malware
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting
industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's
The year 2024 has seen a significant rise in ransomware attacks targeting organizations across various sectors. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the ransomware incidents reported throughout the year, highlighting key metrics and analytics to help understand the scope and impact of these cyber threats.
| Month | Number of Attacks |
|---|---|
| January | 7 |
| February | 24 |
| March | 8 |
| April | 9 |
| May | 5 |
| June | 3 |
| July | 1 |
| August | 0 |
| September | 1 |
| October | 0 |
| November | 0 |
| December | 0 |
| Sector | Number of Attacks |
|---|---|
| Business Services | 21 |
| Technology | 16 |
| Manufacturing | 11 |
| Transportation/Logistics | 7 |
| Government (Religious Organization) | 3 |
| Ransomware Group | Number of Attacks |
|---|---|
| Lockbit3 | 23 |
| Blackbasta | 20 |
| 8base | 10 |
| Rhysida | 2 |
| Unsafe | 2 |
| Sector | Total Data Compromised (GB) |
|---|---|
| Business Services | 15,600 |
| Technology | 9,800 |
| Manufacturing | 7,200 |
| Transportation/Logistics | 3,400 |
| Government (Religious Organization) | 500 |
The year 2024 has been marked by a surge in ransomware attacks, affecting organizations across various sectors. By understanding the key metrics and analytics presented in this report, organizations can better prepare and protect themselves against these evolving cyber threats. Enhanced cybersecurity measures, incident response plans, and collaboration with authorities are crucial steps in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks.

Cybersecurity researchers are raising alarms about ongoing exploitation attempts targeting a recently disclosed vulnerability in Synacor’s Zimbra Collaboration platform.
According to enterprise security firm Proofpoint, exploitation activity started on September 28, 2024. Attackers are aiming to exploit CVE-2024-45519, a critical flaw in Zimbra’s postjournal service that allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands on vulnerable systems.
“The spoofed emails, posing as Gmail, were sent to fake addresses in the CC fields to trick Zimbra servers into parsing and executing them as commands,” Proofpoint shared in a series of posts on X. The spoofed addresses included Base64-encoded strings that Zimbra executed with the sh utility.
The flaw was patched by Zimbra in versions 8.8.15 Patch 46, 9.0.0 Patch 41, 10.0.9, and 10.1.1, released on September 4, 2024, thanks to the discovery by security researcher lebr0nli (Alan Li).
Although the postjournal service may not be enabled on all systems, Ashish Kataria, a security engineer at Synacor, emphasized the importance of applying the patch to prevent potential exploitation. As a temporary measure for systems without the patch, removing the postjournal binary could be considered.
Proofpoint also revealed that the CC’d addresses, once decoded, attempt to plant a web shell at /jetty/webapps/zimbraAdmin/public/jsp/zimbraConfig.jsp, allowing command execution or file downloads over a socket connection.
The exploitation began after Project Discovery published technical details, revealing that the vulnerability stems from unsanitized user input being passed to popen, allowing attackers to inject commands.
In light of these active attacks, it’s critical for Zimbra users to apply the latest patches immediately to safeguard against these threats.

In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, staying informed about the latest campaigns and their methodologies is crucial for maintaining robust security measures. A recent threat report published by AlienVault on February 12, 2025, sheds light on a significant campaign known as REF7707. This report, titled ‘From South America to Southeast Asia: The Fragile Web of REF7707,’ provides valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by this actor group.
The REF7707 campaign is notable for its well-engineered and highly capable intrusion set. However, despite its advanced capabilities, the campaign has been marred by poor management and inconsistent evasion practices. This discrepancy highlights a critical aspect of cybersecurity: even the most sophisticated threats can be mitigated if their execution is flawed.
The report details 399 connected elements, offering a comprehensive view of the campaign’s infrastructure and methodologies. The actor group behind REF7707 has demonstrated a novel approach to intrusion, making it essential for security operation centers (SOCs) to understand these tactics to better defend against similar threats in the future.
One of the key takeaways from this report is the importance of consistent evasion practices. While the campaign’s initial intrusion set was highly capable, the lack of consistency in evading detection allowed security teams to identify and mitigate the threat more effectively. This underscores the need for continuous monitoring and adaptive security measures that can detect and respond to evolving threats.
The report also emphasizes the global reach of the REF7707 campaign, spanning from South America to Southeast Asia. This geographical diversity indicates that no region is immune to sophisticated cyber threats, and organizations worldwide must remain vigilant. The campaign’s ability to target multiple regions highlights the need for a unified approach to cybersecurity, where information sharing and collaboration are paramount.
For SOCs, this report serves as a reminder of the importance of threat intelligence. By staying informed about the latest campaigns and their TTPs, security teams can proactively defend against potential threats. The report provides valuable insights into the REF7707 campaign’s infrastructure, allowing SOCs to identify similar patterns in future attacks.
In addition to understanding the threat landscape, SOCs must also focus on improving their evasion detection capabilities. Consistent and effective evasion practices are crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. By analyzing the flaws in the REF7707 campaign’s execution, SOCs can enhance their own strategies to better detect and mitigate similar threats.
The report is highly reliable, with a confidence level of 100% and a reliability rating of A – Completely reliable. This ensures that the information provided is accurate and trustworthy, making it an invaluable resource for security professionals.
For further reading, the report includes external references to additional resources:
– https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/fragile-web-ref7707
– https://otx.alienvault.com/pulse/67ad1528608f24b71bcea41b
These links provide more detailed information on the REF7707 campaign and its implications for cybersecurity.
In conclusion, the ‘From South America to Southeast Asia: The Fragile Web of REF7707’ report offers a comprehensive analysis of a sophisticated yet flawed cyber threat. By understanding the TTPs employed by this actor group and learning from their mistakes, SOCs can enhance their security measures and better protect against future threats.
Recommendations for Mitigation:
1. Enhance Threat Intelligence: Stay updated with the latest threat reports and intelligence to understand emerging threats and their TTPs.
2. Improve Evasion Detection: Implement robust evasion detection mechanisms to identify and mitigate sophisticated threats effectively.
3. Foster Collaboration: Encourage information sharing and collaboration within the cybersecurity community to build a unified defense against global threats.
4. Continuous Monitoring: Maintain continuous monitoring of network activities to detect and respond to potential threats promptly.
5. Adaptive Security Measures: Develop adaptive security measures that can evolve with changing threat landscapes.
By following these recommendations, SOCs can strengthen their defenses and better protect against the ever-evolving cyber threats.

Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.